Understanding Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
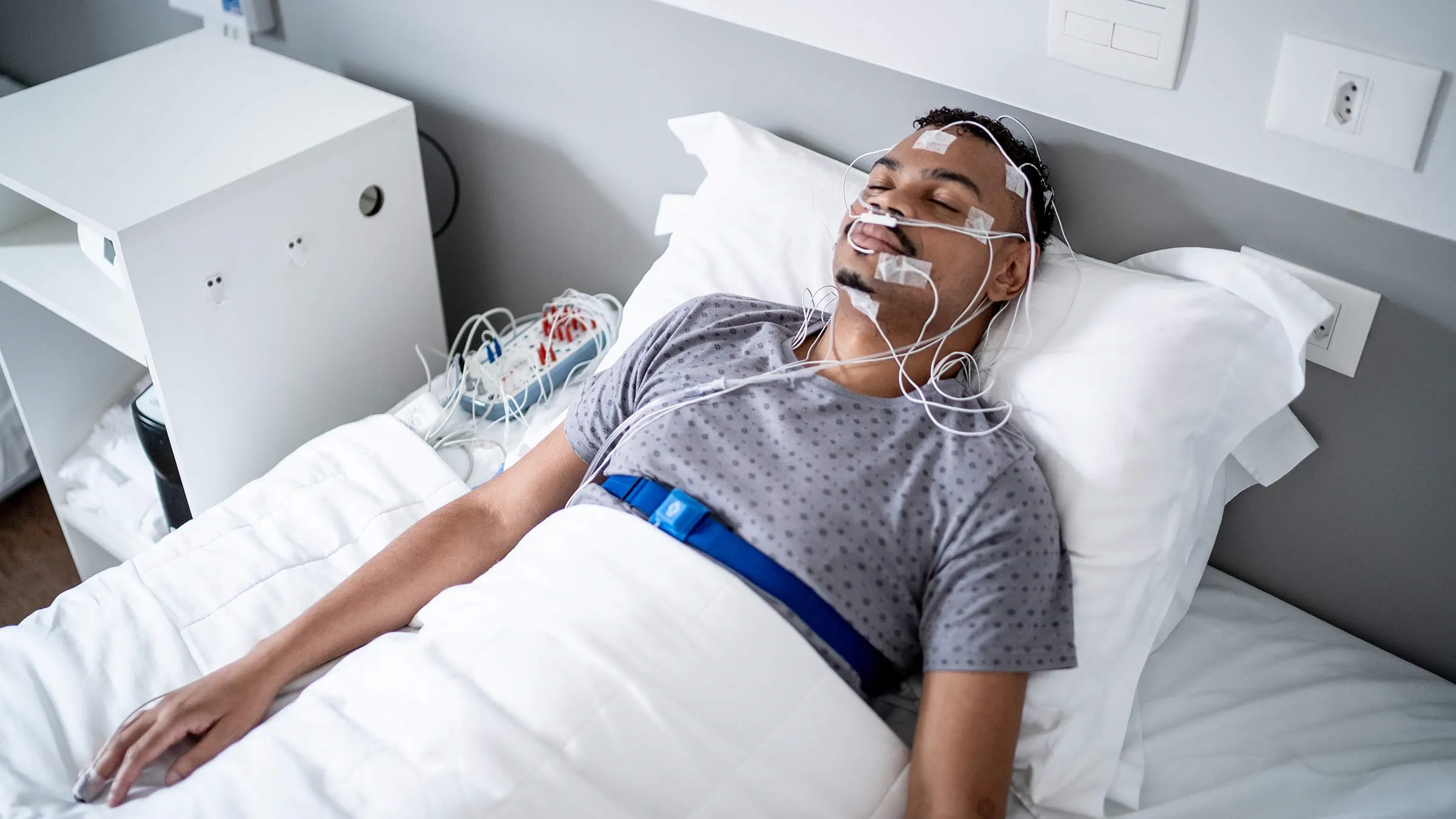
Sleep is one of the most vital pillars of good health, but for millions of people, restful sleep is harder to achieve than it should be. One of the most common reasons for poor sleep quality is sleep apnea, a potentially serious sleep disorder that often goes undiagnosed.
If you’ve ever been told you snore loudly, gasp for air during sleep, or feel unusually tired during the day, sleep apnea might be the cause. In this article, we’ll explore what sleep apnea is, its causes, symptoms, and the most effective treatment options — from simple lifestyle changes to advanced therapies.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where a person’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. These pauses can last from a few seconds to a minute and may occur dozens of times throughout the night.
There are three main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) – The most common type, caused by blockage of the airway due to relaxed throat muscles.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) – Occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to muscles controlling breathing.
- Complex or Mixed Sleep Apnea – A combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Regardless of the type, the result is the same — disrupted sleep and reduced oxygen levels that can impact overall health.
The Hidden Dangers of Sleep Apnea
While many people dismiss snoring as harmless, untreated sleep apnea can lead to serious health complications, including:
- High blood pressure and heart disease
- Stroke or irregular heart rhythms
- Type 2 diabetes
- Chronic fatigue and mood disorders
- Cognitive decline and memory problems
When breathing repeatedly stops during the night, oxygen levels drop, forcing the heart and brain to work harder. Over time, this strain can significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Common Causes of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can affect anyone, but certain factors increase your risk. Here are the most common causes and risk factors:
1. Excess Weight
Carrying extra fat around the neck can narrow the airway, making it harder to breathe at night. Obesity is one of the leading causes of obstructive sleep apnea.
2. Anatomical Factors
Some people naturally have smaller airways, enlarged tonsils, or a thick neck structure, which can restrict airflow during sleep.
3. Age and Gender
Sleep apnea is more common in men and tends to increase with age, although women are also at risk, especially after menopause.
4. Family History
A family history of sleep apnea can increase your chances of developing the condition, particularly if similar facial or airway structures are inherited.
5. Lifestyle Habits
Smoking, alcohol consumption, and sedative use relax throat muscles, making airway collapse more likely during sleep.
6. Medical Conditions
Certain conditions like nasal congestion, hypothyroidism, and neuromuscular disorders can contribute to airway obstruction or irregular breathing patterns.
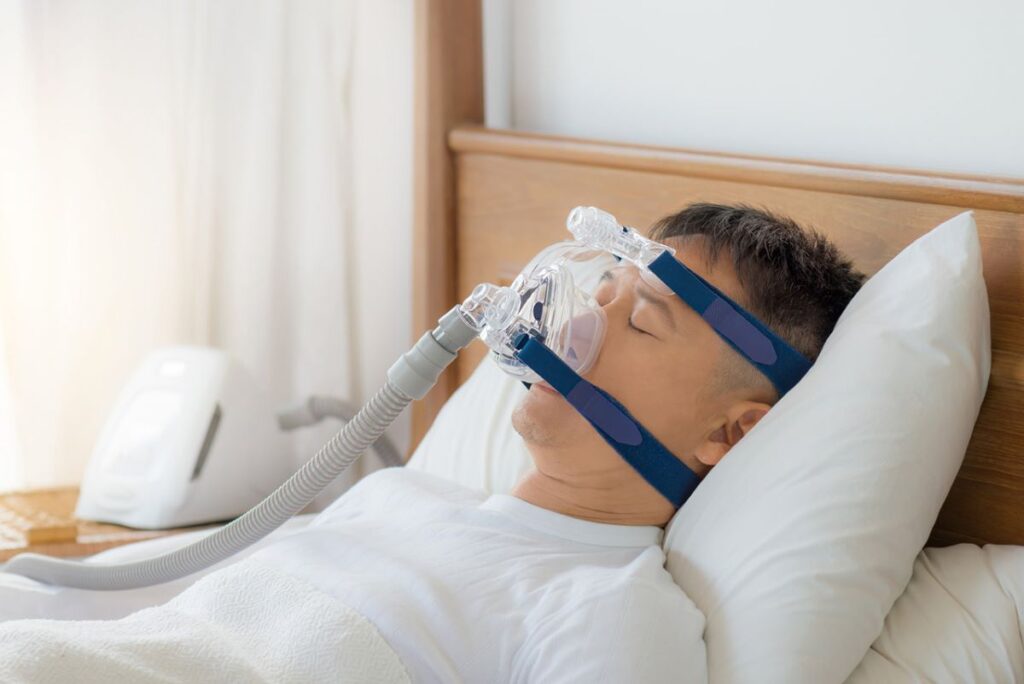
Table of Contents
ToggleRecognizing the Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea often goes undetected because the person affected may not remember waking up throughout the night. However, common symptoms include:
- Loud, chronic snoring
- Pauses in breathing observed by a partner
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Daytime fatigue or falling asleep during routine activities
- Morning headaches
- Irritability, mood swings, or depression
- Poor concentration and memory problems
If you or your partner notice these signs, it’s important to consult a doctor or sleep specialist for further evaluation.
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea: The Role of Sleep Studies
A sleep study (also known as polysomnography) is the gold standard for diagnosing sleep apnea. This test can be done either at a sleep clinic or through an at-home sleep test.
In-Lab Sleep Study
During a clinic-based sleep study, sensors are attached to monitor:
- Breathing patterns
- Brain activity (EEG)
- Oxygen levels
- Heart rate
- Leg and eye movements
At-Home Sleep Test
For mild to moderate cases, doctors may recommend a simplified home-based version that records breathing, oxygen, and airflow data overnight.
Both methods help determine the severity of sleep apnea and guide treatment options.
Effective Treatments for Sleep Apnea
Treatment depends on the type and severity of your sleep apnea, but the goal is always the same — to keep your airway open and improve oxygen flow during sleep. Let’s explore the most effective options.
1. CPAP Therapy (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure)
The CPAP machine is the most common and effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. It delivers a steady stream of air through a mask, preventing airway collapse.
Benefits of CPAP therapy:
- Reduces snoring and daytime sleepiness
- Improves sleep quality and energy levels
- Decreases the risk of heart disease and high blood pressure
Though it can take time to adjust, most users experience significant improvement within days.
2. Oral Appliances
For mild to moderate sleep apnea, oral appliances are a great alternative to CPAP. These custom-fitted devices reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open.
They’re ideal for people who travel frequently or find CPAP masks uncomfortable.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes can have a big impact on managing sleep apnea symptoms:
- Lose excess weight to reduce pressure on the airway
- Sleep on your side instead of your back
- Avoid alcohol and sedatives before bedtime
- Quit smoking, as it increases inflammation and airway swelling
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule
4. Surgery
In severe or treatment-resistant cases, surgery may be recommended to remove or reduce tissue blocking the airway. Common procedures include uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), nasal surgery, or jaw repositioning.
5. Emerging Treatments
Modern medicine continues to advance sleep apnea care. Inspire therapy, a newer treatment, uses a small implanted device that stimulates airway muscles to prevent collapse — offering a high-tech alternative to traditional methods.
Living Well with Sleep Apnea
Managing sleep apnea isn’t just about better sleep — it’s about improving your quality of life. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, most people experience:
- More energy and alertness
- Improved mood and focus
- Lower risk of heart problems
- Better relationships due to reduced snoring and restlessness
Early diagnosis and consistent treatment can make a world of difference.
Final Thoughts
Sleep apnea is more than just loud snoring — it’s a serious medical condition that affects your overall health and well-being. The good news is that with the right approach — from CPAP therapy and oral appliances to lifestyle changes — it’s completely manageable.
If you suspect you or a loved one has sleep apnea, talk to a sleep specialist and consider getting a sleep study. The sooner you act, the sooner you can reclaim restful, healthy sleep.
FAQS
Sleep apnea is often caused by airway obstruction during sleep, excess weight, nasal congestion, or anatomical issues in the throat. It can also result from neurological conditions that disrupt breathing signals between the brain and body.
Common symptoms include loud snoring, choking or gasping during sleep, daytime fatigue, morning headaches, and difficulty concentrating. If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to more serious health problems like heart disease or high blood pressure.
A sleep specialist usually diagnoses sleep apnea through an overnight sleep study (polysomnography) or a home-based sleep test. These tests record your breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and heart rate to identify the severity of your sleep disorder.
Treatment options include CPAP therapy, oral appliances, lifestyle changes (like losing weight or avoiding alcohol), and in severe cases, surgery. The right approach depends on the type and severity of your sleep apnea.
Sleep is one of the most vital pillars of good health, but for millions of people, restful sleep is harder to achieve than it should be. One of the most common reasons for poor sleep quality is sleep apnea, a potentially serious sleep disorder that often goes undiagnosed. If you’ve ever been told you snore…
Recent Posts
 Home vs. Portable: Can One Oxygen Concentrator Do Both?Home vs. Portable: Can One Oxygen Concentrator Do Both? For many Australians managing chronic respiratory conditions like COPD or emphysema, the quest for the “perfect” oxygen setup often leads to one critical question: Can one oxygen […]
Home vs. Portable: Can One Oxygen Concentrator Do Both?Home vs. Portable: Can One Oxygen Concentrator Do Both? For many Australians managing chronic respiratory conditions like COPD or emphysema, the quest for the “perfect” oxygen setup often leads to one critical question: Can one oxygen […] Understanding Your Sleep Study Report: What the Results MeanThis guide explains what those results typically mean, so they can follow the logic of the report before discussing next steps with a clinician. What is a sleep study report actually measuring? A sleep study report explains how they sleep and how their […]
Understanding Your Sleep Study Report: What the Results MeanThis guide explains what those results typically mean, so they can follow the logic of the report before discussing next steps with a clinician. What is a sleep study report actually measuring? A sleep study report explains how they sleep and how their […] Sleep Apnea Test Adelaide: 5 Signs You Should Book OneIf they live in Adelaide and recognise the signs below, booking a sleep apnoea test is often the fastest way to get clarity and start feeling better. What exactly is sleep apnoea, and why does testing matter? A sleep apnea test Adelaide service is used […]
Sleep Apnea Test Adelaide: 5 Signs You Should Book OneIf they live in Adelaide and recognise the signs below, booking a sleep apnoea test is often the fastest way to get clarity and start feeling better. What exactly is sleep apnoea, and why does testing matter? A sleep apnea test Adelaide service is used […] Ultimate Guide to Choosing an Oxygen Concentrator in Australia (2026)ntroduction to Modern Oxygen Therapy For many Australians living with chronic respiratory conditions, maintaining an active lifestyle in cities like Sydney requires more than just medical advice—it requires the right technology. An oxygen concentrator is […]
Ultimate Guide to Choosing an Oxygen Concentrator in Australia (2026)ntroduction to Modern Oxygen Therapy For many Australians living with chronic respiratory conditions, maintaining an active lifestyle in cities like Sydney requires more than just medical advice—it requires the right technology. An oxygen concentrator is […]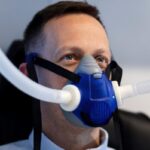 The Best CPAP Mask Options for New Users and What Makes Them ComfortableSleep apnea disrupts breathing during sleep, causing repeated pauses that prevent restful sleep and strain the cardiovascular system. CPAP therapy delivers continuous pressurized air through a mask, keeping airways open throughout the night and enabling […]
The Best CPAP Mask Options for New Users and What Makes Them ComfortableSleep apnea disrupts breathing during sleep, causing repeated pauses that prevent restful sleep and strain the cardiovascular system. CPAP therapy delivers continuous pressurized air through a mask, keeping airways open throughout the night and enabling […] Oxygen Machine for Home Use: A Complete Guide for First-Time BuyersWhat Is an Oxygen Machine and How Does It Work? An oxygen machine for home use, commonly known as an oxygen concentrator, is a medical device that delivers concentrated oxygen to individuals with respiratory conditions. These respiratory therapy devices […]
Oxygen Machine for Home Use: A Complete Guide for First-Time BuyersWhat Is an Oxygen Machine and How Does It Work? An oxygen machine for home use, commonly known as an oxygen concentrator, is a medical device that delivers concentrated oxygen to individuals with respiratory conditions. These respiratory therapy devices […] Medical Oxygen at Home: Essential Information on Oxygen Tanks, Machines, and TherapiesIntroduction For individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD, asthma, or emphysema, medical oxygen therapy at home is often a critical part of maintaining health and improving quality of life. Whether you need an oxygen machine for […]
Medical Oxygen at Home: Essential Information on Oxygen Tanks, Machines, and TherapiesIntroduction For individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD, asthma, or emphysema, medical oxygen therapy at home is often a critical part of maintaining health and improving quality of life. Whether you need an oxygen machine for […]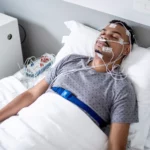 Understanding Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective TreatmentsSleep is one of the most vital pillars of good health, but for millions of people, restful sleep is harder to achieve than it should be. One of the most common reasons for poor sleep quality is sleep apnea, a potentially serious sleep disorder that often […]
Understanding Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective TreatmentsSleep is one of the most vital pillars of good health, but for millions of people, restful sleep is harder to achieve than it should be. One of the most common reasons for poor sleep quality is sleep apnea, a potentially serious sleep disorder that often […] Bulk-Bill Sleep Study Brisbane: Affordable Options for LocalsWhat Are Bulk-Bill Sleep Studies and How Do They Work in Brisbane? Bulk-bill sleep study Brisbane services provide you with direct billing to Medicare, eliminating upfront costs for diagnostic testing. When you receive a bulk-bill sleep study, the […]
Bulk-Bill Sleep Study Brisbane: Affordable Options for LocalsWhat Are Bulk-Bill Sleep Studies and How Do They Work in Brisbane? Bulk-bill sleep study Brisbane services provide you with direct billing to Medicare, eliminating upfront costs for diagnostic testing. When you receive a bulk-bill sleep study, the […] Sleep Apnea Test Adelaide: Early Diagnosis for Better HealthWhat Is Sleep Apnea and Why Is Early Diagnosis Important? Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder where your breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain undiagnosed, missing […]
Sleep Apnea Test Adelaide: Early Diagnosis for Better HealthWhat Is Sleep Apnea and Why Is Early Diagnosis Important? Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder where your breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain undiagnosed, missing […]
Categories
- CPAP Machine
- CPAP Mask Online
- CPAP Masks
- Cpap Masks Australia
- Laser Eye Surgery
- Lasik Surgery
- Medical Oxygen
- Oxygen Concentrator
- Portable Oxygen Concentrator Australia
- Portable Oxygen Concentrator Machine
- ResMed AirMini
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Apnea Test Adelaide
- Sleep Apnea Test Brisbane
- Sleep Study
- Sleep Type Test
- Sydney Eye Clinic
